Estimate the Air Conditioner Capacity
The hot temperature in our country makes it difficult and quite impossible for us to relax comfortably, even when the ceiling fan is set to maximum speed. Even at night, the heat is still felt, making us feel uncomfortable and preventing us from sleeping properly. As a result, installing an air conditioner in the bedroom and living room is the best solution for providing comfort to the entire family.
Previously, having an air conditioner in the house used to be considered a luxury. However, an air conditioner has been classified as one of the needed equipment for most houses in Malaysia. Moreover, an air conditioner is no longer a premium, high-priced product thanks to lower prices and new technologies equipped with energy-saving devices. Panasonic, Mitsubishi, Daikin, Haier and York are among the brands available in the market today.
An air conditioner consists of mechanical components to absorb heat from a closed area and transfer that heat to the outside. A good air conditioner should be able to control and adjust the temperature at a comfortable level (22-27 °C), control relative humidity (40%-60%), control air circulation, and produce clean air in the room. Compressor, condenser, metering device and evaporator are the four main components of an air conditioning system.
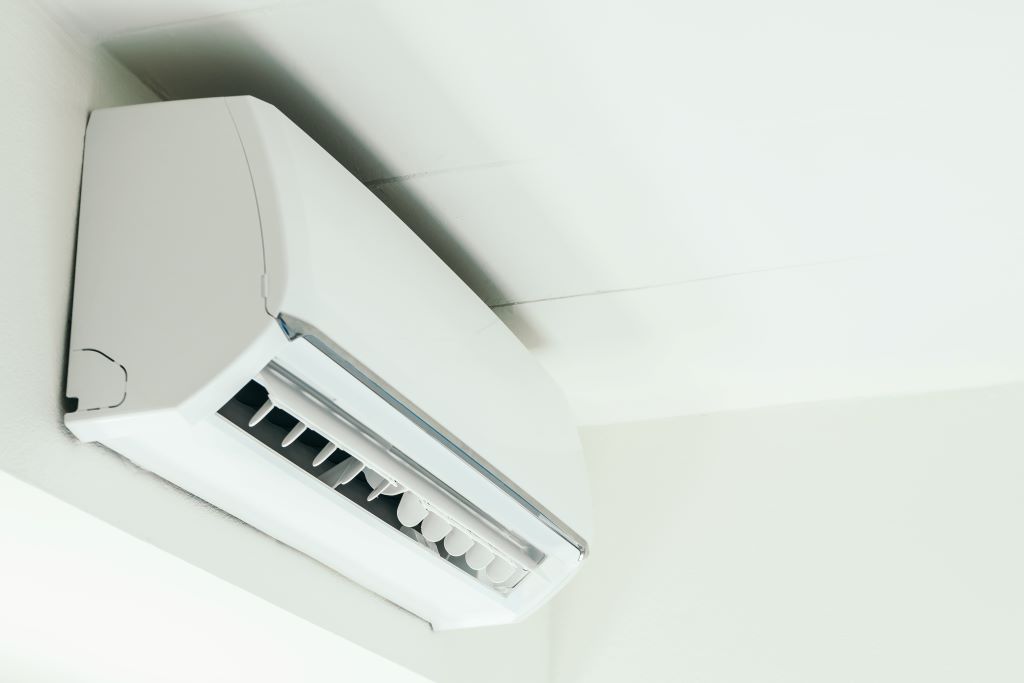
An air conditioner is divided into two main categories, namely for domestic and commercial use. In domestic use, the split unit type that consists of indoor and outdoor units is the most popular and frequently used. A common split unit used in homes is the wall-mounted type, as shown in Figure 1. The capacity of this type is in horsepower (HP) with a selection of 1HP, 1.5HP, 2HP, 2.5HP and 3HP.

Figure 1: Wall-mounted split unit type air conditioner
The selection of the suitable air conditioner HP for a certain room size can be done by obtaining a value of cooling capacity (measured in BTU/hour). The cooling capacity of the air conditioner is based on the size of the evaporator (cooling coil) where the cooling process takes place.
A British thermal unit (BTU) is the energy needed to raise 1 pound of water by 1 °F at sea level. When it comes to air conditioning, the BTU rating indicates how many BTU/hour heats it can remove from the air and determines the cooling power of an air conditioning. The air conditioner HP increases as the BTU value increases. In other words, the BTU defines how much HP is required to cool a room effectively. Usually, a 1HP air conditioner can remove 9,000 BTU/hour of heat. With better technology, some air conditioners can remove up to 10,000 BTU/hour of heat with the same capacity (for calculation purpose, 1 HP ≡ 9,500 BTU/hour). Errors in determining the BTU can result in the air conditioner purchased having less power or more power, which will affect later. The most straightforward method to determine BTU is to use a calculator given by the air conditioner company. However, a few methods can and are frequently used to estimate BTU value and then obtain the HP value of the air conditioner.
Method 1: Simple cooling capacity estimation using area only
So, the suitable air conditioner capacity for this room is 1.5HP
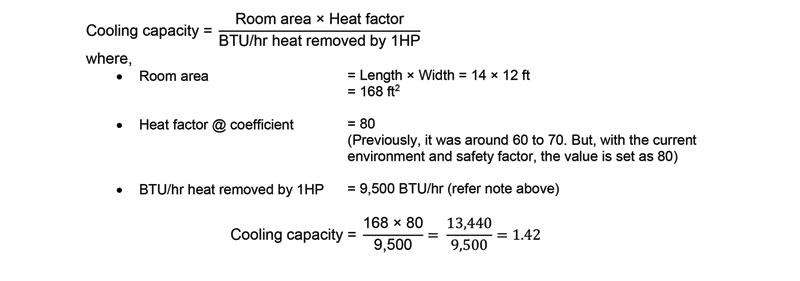
Method 2: Simple cooling capacity estimation using area and height

So, the suitable air conditioner capacity for this room is 1.5HP
Method 3: Air conditioning estimation – Rule of thumb
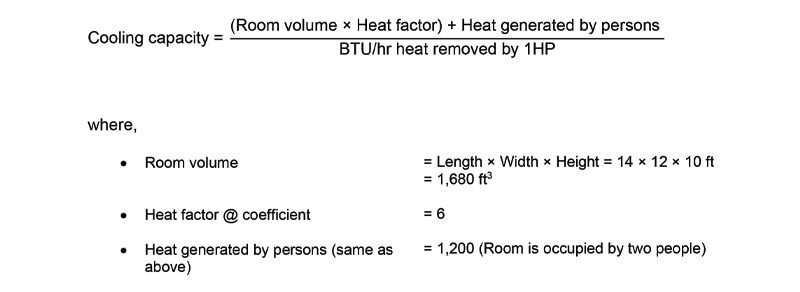
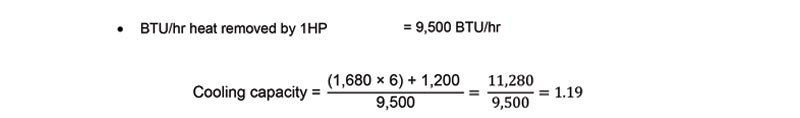
So, the suitable air conditioner capacity for this room is 1.5HP
Of the three methods, all give the same result: an air conditioner with 1.5HP is the most suitable capacity installed for the room shown in Figure 2. However, in order to acquire a more accurate BTU value, some additional factors should be considered, which are:
- Heat generated by other electrical appliances or electronic devices in the room such as lighting, PC or laptop, television (if any).
- Heat generated by persons. All the calculations above are based on two people only. The more person occupies the room will generate more heat.
- The location and size of the windows. It is related to direct sunlight exposure.
- Air leak in the room.
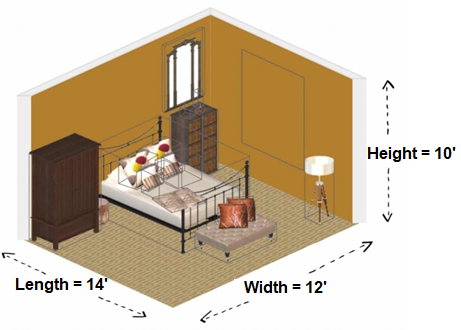
Figure 2: Room Size (for calculation example)
The following is reference values that can be used as a heat factor and for additional factor to consider when determining the BTU:
- Lighting, electrical appliances or electronic + (watt × 3.5)
- Next person in the room + 600 BTU for each person
- Room is direct to the sunlight + (10% from the total BTU)
- Open area, room Area × 120
- Kitchen area (equipment like stove, fridge and oven) + 4,000 BTU
However, a ceiling fan can assist in lowering BTU usage by improving air circulation.

The writer is a Senior Vocational Training Officer, Centre for Design & Innovation of Technology (PRInT), Universiti Malaysia Pahang (UMP).
E-mail: junaedi@ump.edu.my
- 27622 views










